Shoulder Arthroplasty
Shoulder Arthroplasty
Total shoulder arthroplasty represents the premier therapeutic option offered by modern orthopedic surgery for addressing advanced pathologies of the shoulder joint. According to the most recent scientific studies (2024), reverse total shoulder arthroplasty (RTSA) demonstrates excellent results with a 94% success rate in follow-up of at least 5 years.
The main indications include osteoarthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, osteonecrosis, rotator cuff arthropathy, and complex shoulder fractures that cause severe pain and significant limitation of upper extremity functionality.
Scientific Evidence & Results
Recent clinical studies from the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (2024) confirm that reverse total shoulder arthroplasty offers satisfactory medium-term results for various pathologies, while long-term follow-up data show stable improvement in functionality.
According to a study by the National Institutes of Health (NIH, 2024), patients aged 85 years and older can expect significant improvement in shoulder function and significant pain reduction after reverse total shoulder arthroplasty, with an overall complication rate of only 14.7%.
What is Reverse Shoulder Arthroplasty
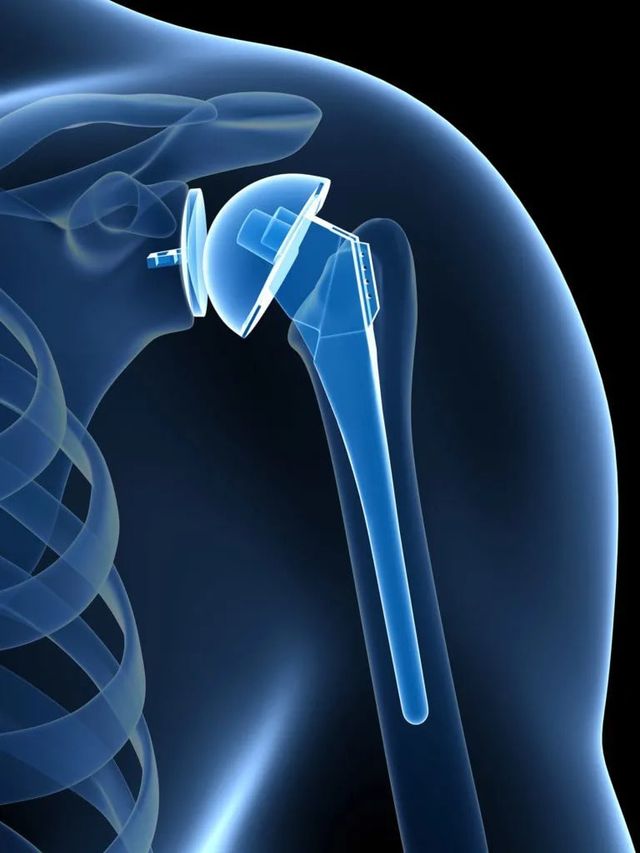
Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty is an innovative surgical technique developed in Europe in the 1980s and approved by the FDA for use in the United States in 2004. This technique reverses the anatomical relationship of the articular surfaces.
Surgical Technique: We replace the articular surfaces in reverse of their anatomical relationship. In place of the glenoid, a metallic sphere (glenosphere) is positioned, and in place of the humeral head, a concave surface of high-density polyethylene supported by a titanium stem is placed.
Biomechanical Advantage: In this way, the concave surface of the humerus moves on the sphere of the glenoid, allowing the deltoid muscle to assume the function of the damaged rotator cuff and provide stability and movement to the joint.
Clinical Indications & Patient Selection
According to the most recent clinical guidelines, reverse shoulder arthroplasty is the treatment of choice for:
The Surgical Procedure
Preoperative Planning
Includes detailed imaging evaluation with CT scan and 3D reconstruction for accurate determination of anatomy and selection of appropriate prosthesis sizes.
Surgical Technique
The procedure is performed through a deltopectoral approach with a duration of approximately 2 hours. Modern prosthetic systems with cementless fixation are used for long-term stability.
Anesthesia & Postoperative Analgesia
General anesthesia combined with interscalene nerve block for optimal postoperative analgesia and faster recovery.
Clinical Outcomes & Prognosis
Long-term Results
Follow-up studies over 10 years show maintenance of clinical results with prosthesis survival rates of 94% at 5 years and 89% at 10 years.
Functional Outcomes
Significant improvement in functional assessment scales (Constant-Murley Score, ASES Score) with mean improvement of 40-50 points postoperatively.
Pain Relief
Over 95% of patients report significant pain relief with VAS scores below 2/10 in long-term follow-up.
Rehabilitation Program
Phase I (0-6 weeks)
Phase II (6-12 weeks)
Phase III (3-6 months)
Complications & Management
The overall complication rate is relatively low (14.7% according to recent studies), while prosthesis survival is excellent with a 94% rate in follow-up of at least 5 years.
Mechanical Complications
Include prosthetic loosening, polyethylene wear, and periprosthetic fractures. Modern cementless fixation technology has significantly reduced these complications.
Infections
Infection rate below 2%. Prophylactic antibiotic therapy and strict adherence to aseptic principles are crucial for prevention.
Neurological Complications
Transient axillary nerve injury in <5% of cases, usually with complete recovery within 6-12 months.
Clinical image of patient after successful reverse shoulder arthroplasty
Modern Developments & Innovations
Personalized Prostheses
Use of 3D printing and patient-specific instrumentation for optimal fit and long-term results.
Minimally Invasive Techniques
Smaller incisions, reduced soft tissue damage, and faster recovery using specialized surgical instruments.
Improved Materials
Next-generation ceramics and metal alloys with increased wear resistance and biocompatibility.
Return to Activities
Recent studies (2024) show that patients who have undergone reverse total shoulder arthroplasty demonstrate high rates of return to work and sports.
6-8 weeks
Daily activities (dressing, eating, personal hygiene)
3-4 months
Return to work (office), driving
6-12 months
Low-risk sports activities (swimming, golf, tennis)
Conclusions
Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty represents an effective and reliable surgical option for managing complex shoulder joint pathologies. The excellent clinical results, low complication frequency, and high patient satisfaction make it the treatment of choice for selected patients.
The success of the procedure depends on proper patient selection, precise surgical technique, and systematic rehabilitation program. The continuous evolution of technology and surgical techniques promises even better results in the future.